The demand for a cybersecurity career has never been higher. As businesses and governments continue to rely on digital infrastructure, cyber threats are growing in both complexity and frequency. According to industry reports, cybercrime is projected to cost the global economy trillions of dollars annually, pushing companies to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures.
Increasing Demand and Competitive Salaries
Organizations across industries—from finance and healthcare to government and retail—are actively seeking cybersecurity professionals to protect their systems and data. Reports indicate a global shortage of cybersecurity talent, with millions of unfilled positions. This demand translates into competitive salaries; for example, roles such as Cloud Security Engineer can command salaries exceeding $120,000 per year.
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and supply chain vulnerabilities becoming more sophisticated. As a result, cybersecurity professionals must stay ahead of attackers by continuously learning and adapting to new technologies and strategies.
Employer Expectations: A Blend of Technical and Soft Skills
Employers are looking for professionals who not only have a strong technical foundation but also possess problem-solving abilities, adaptability, and communication skills. Cybersecurity teams often collaborate with different departments, making clear communication and teamwork essential in the field.
How to start a cybersecurity career?

To secure a cybersecurity job, professionals must develop a strong technical foundation. The following skills are considered essential for building a successful career in cybersecurity:
Network Security
Network security is the backbone of cybersecurity. Professionals must understand how to secure wired and wireless networks against threats such as unauthorized access, malware, and data breaches. Key aspects include:
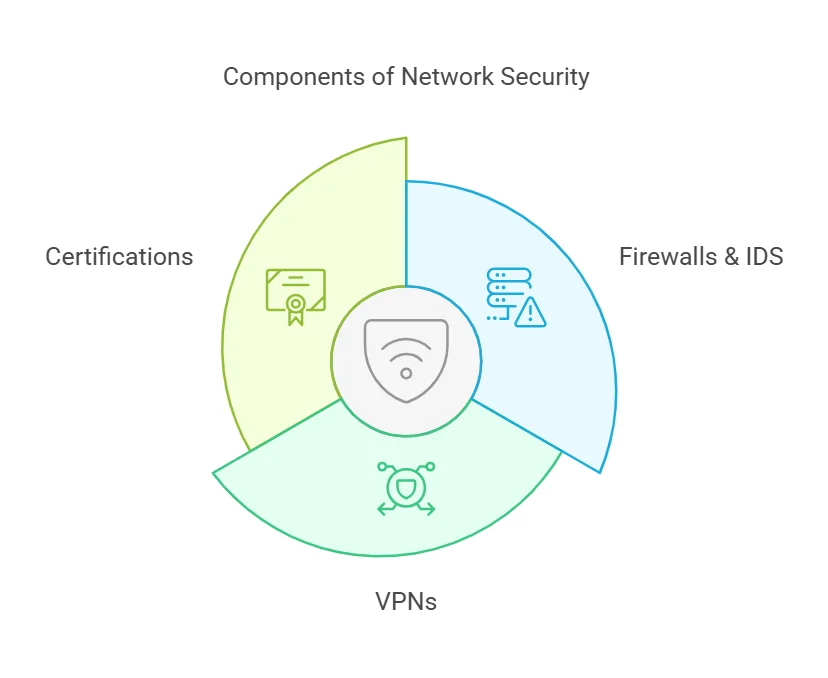
- Firewalls & Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Protecting networks from unauthorized access.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Ensuring encrypted and secure communication.
- Certifications: CompTIA Security+, Cisco CCNA.
Cloud Security
With businesses rapidly migrating to cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, understanding cloud security is a must. Employers seek professionals who can:
- Secure cloud-based applications and data.
- Implement access control and encryption measures.
- Understand compliance requirements for cloud environments.
- Benefit: Professionals with cloud security expertise earn a salary premium of $15,000+.
Programming & Coding
Cybersecurity experts often need to write scripts for automating security tasks, analyzing threats, and identifying vulnerabilities. Key programming skills include:
- Python & PowerShell: Used for security automation.
- Java & JavaScript: Essential for securing web applications.
- SQL: Protecting databases from attacks like SQL injection.
Operating Systems & Digital Forensics
Understanding multiple operating systems is crucial for securing endpoints and investigating security incidents. Key areas include:
- Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android: Understanding security configurations and vulnerabilities.
- Kali Linux: Popular for penetration testing and ethical hacking.
- Digital forensics: Analyzing compromised systems and recovering lost data.
Incident Response & Threat Intelligence
Cybersecurity professionals must be able to detect, analyze, and respond to security incidents in real-time. Skills in this area include:
- Incident response frameworks: NIST and SANS guidelines for structured response.
- Threat intelligence analysis: Understanding attack patterns and hacker tactics.
- Malware analysis: Identifying and mitigating malicious software threats.
AI & Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used to predict and prevent cyber threats. Professionals with AI skills can:
- Use machine learning models to detect anomalies in network traffic.
- Automate security responses with AI-driven cybersecurity tools.
- Analyze large datasets for proactive threat detection.
Penetration Testing & Ethical Hacking
Penetration testers simulate cyberattacks to find vulnerabilities before real attackers do. This field requires:
- Knowledge of hacking techniques and tools.
- Certifications like CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) and OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional).
- Hands-on experience with penetration testing frameworks.
Additional Technical Skills in Demand
- Application Security Development (DevSecOps)https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/devsecops/: Integrating security into software development.
- Risk and Compliance Auditing: Ensuring adherence to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Managing secure authentication and access control.
The Importance of Soft Skills in Cybersecurity

While technical expertise is the backbone of a cybersecurity career, soft skills are just as crucial. Cybersecurity professionals often work in teams, communicate with stakeholders, and make high-pressure decisions. The ability to think critically, adapt to evolving threats, and explain security issues in simple terms can set a candidate apart in a competitive job market.
Communication Skills
Cybersecurity threats impact entire organizations, not just IT teams. Professionals must be able to:
- Translate technical issues into non-technical language for executives and employees.
- Write clear and concise incident reports and security policies.
- Effectively present findings and recommendations in meetings.
Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving
Cybersecurity requires the ability to analyze threats and respond quickly. Professionals need to:
- Evaluate risks and anticipate potential attack vectors.
- Think like a hacker to identify vulnerabilities before attackers do.
- Use logical reasoning to investigate security incidents and determine root causes.
Adaptability & Continuous Learning
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, meaning cybersecurity professionals must:
- Stay updated on the latest attack trends and security tools.
- Quickly learn new technologies and programming languages as needed.
- Adjust strategies to counter emerging threats like AI-powered attacks.
Attention to Detail
A single overlooked vulnerability can lead to a security breach. Cybersecurity professionals must:
- Thoroughly analyze logs and alerts for suspicious activity.
- Review code and configurations for security loopholes.
- Ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
Teamwork & Collaboration
Cybersecurity is a team effort, requiring professionals to work with:
- IT and software development teams to integrate security into systems.
- Legal and compliance departments to meet regulatory standards.
- Non-technical staff to promote cybersecurity awareness and best practices.
Soft skills are the key to becoming an effective cybersecurity professional, as they enhance collaboration, decision-making, and overall security posture.
Certifications & Training to Boost Your Cybersecurity Career

Certifications are one of the best ways to validate your cybersecurity skills and stand out to employers. They demonstrate technical expertise, practical experience, and a commitment to continuous learning.
Entry-Level Certifications (For Beginners & Career Changers)
If you’re new to cybersecurity, start with foundational certifications such as:
- CompTIA Security+ – Covers basic security concepts, risk management, and network security.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) – Focuses on penetration testing and ethical hacking techniques.
- Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate – Teaches cybersecurity operations and network defense fundamentals.
Intermediate Certifications (For Those with Some Experience)
Once you have basic experience, consider these mid-level certifications:
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) – Covers security architecture, risk management, and incident response.
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) – Focuses on cloud security best practices for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC) – Covers hands-on security skills, including threat detection and prevention.
Advanced & Specialized Certifications (For Experienced Professionals)
For those looking to specialize, advanced certifications include:
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) – Highly regarded penetration testing certification requiring hands-on hacking skills.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) – Best for cybersecurity managers and leaders focused on governance and risk management.
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) – Geared toward professionals focusing on auditing and compliance.
Specialized Training Programs
- SANS Cybersecurity Training – Offers a variety of hands-on courses in penetration testing, digital forensics, and incident response.
- Coursera & Udemy Courses – Provide online training for cybersecurity fundamentals, ethical hacking, and cloud security.
- Microsoft & AWS Security Certifications – Focused on securing cloud environments, ideal for cloud security professionals.
Emerging Trends & Future Skills in Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging alongside technological advancements. To stay competitive, professionals must adapt and develop skills in cutting-edge security domains.
AI & Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
AI is transforming cybersecurity by automating threat detection and response. Professionals should:
- Learn about AI-driven security tools like endpoint detection and response (EDR).
- Understand machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection and predictive threat analysis.
- Stay informed on the risks of AI-powered cyberattacks and how to defend against them.
Cloud & Zero Trust Security
As companies shift to the cloud, security professionals need expertise in:
- Cloud security frameworks (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Zero Trust Architecture, which requires strict verification for every user and device.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) to prevent unauthorized access.
Blockchain & Cryptography
Blockchain is gaining traction for securing transactions and digital identities. Key areas to focus on:
- Decentralized security models for data protection.
- Cryptographic algorithms used in blockchain and secure communications.
- Smart contract security to prevent exploitation in blockchain applications.
IoT & Mobile Security
The rapid expansion of IoT devices introduces new vulnerabilities. Future cybersecurity skills include:
- Securing connected devices in healthcare, smart homes, and industrial systems.
- Detecting and preventing mobile malware and SIM swap attacks.
- Implementing endpoint security solutions to manage diverse device networks.
Regulatory Compliance & Risk Management
With increasing cybersecurity regulations, professionals should develop expertise in:
- Data privacy laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Risk assessment frameworks to ensure compliance.
- Security governance policies for protecting sensitive information.
As cybersecurity threats evolve, professionals must embrace continuous learning and emerging technologies to stay ahead.
Conclusion

A career in cybersecurity requires a combination of technical expertise, soft skills, and continuous learning. Foundational skills like network security, cloud security, and programming are essential, while soft skills like communication, critical thinking, and adaptability ensure long-term success.
Certifications such as CompTIA Security+, CISSP, and OSCP can boost your credentials and improve job prospects. Meanwhile, staying ahead of emerging trends—including AI-driven security, blockchain, IoT protection, and Zero Trust models—is crucial for future-proofing your career.
Cybersecurity is an exciting and high-demand field with opportunities in ethical hacking, incident response, threat intelligence, and cloud security. Whether you’re starting out or looking to advance, continuous skill development and hands-on experience will keep you competitive in this ever-evolving industry.
Ready to launch your cybersecurity career? Start by building your skills, earning certifications, and staying updated on the latest security trends.