OpenAI has introduced Study Mode for ChatGPT, marking a significant shift in how artificial intelligence is positioned within educational settings. Launched on July 29, 2025, this feature represents OpenAI’s proactive response to growing concerns about AI-assisted academic dishonesty while attempting to reframe AI as a constructive educational tool rather than a shortcut for assignments.
- The Rise of AI Cheating in Educational Institutions
- Study Mode: Technical Architecture and Pedagogical Approach
- Core Features and Functionality
- System Architecture
- Educational Impact and Research Findings
- Positive Educational Outcomes
- Challenges and Limitations
- Global Implementation and Institutional Responses
- Competitive Landscape and Industry Response
- Limitations and Critical Perspectives
- Future Directions and Implications
- Educational Policy Implications
- Research Gaps and Future Studies
- Conclusion
The Rise of AI Cheating in Educational Institutions
The educational landscape has been fundamentally disrupted by the widespread adoption of AI tools, with concerning trends in academic integrity violations. Recent data reveal that AI cheating rates in UK educational institutions have surged dramatically, from 1.6 per 1,000 students in 2022-23 to 5.1 per 1,000 students in 2023-24, with current estimates reaching 7.5 per 1,000 students in 2024-25. This represents more than a four-fold increase in just two years.
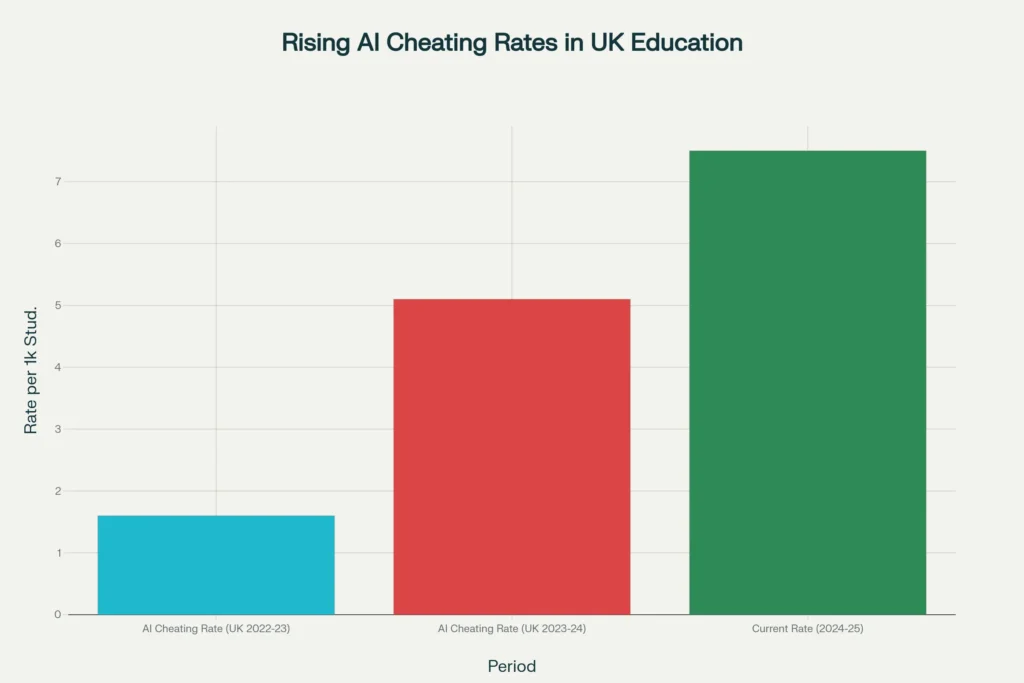
Rising trend of AI cheating incidents in UK educational institutions from 2022-23 to 2024-25, showing rates per 1000 students
Globally, approximately 56% of college students have admitted to using AI tools on assignments or exams, while over half (54%) of these students acknowledge that such usage constitutes cheating or plagiarism. The situation is particularly acute in higher education, where more than one-third of US college-age adults use ChatGPT, with a quarter of messages related to learning and homework.
The scope of the problem extends beyond simply completing assignments. A Guardian survey identified nearly 7,000 verified cases of AI-related cheating in the UK during the 2023-24 academic year alone. Academic institutions worldwide report varying levels of AI misuse, with Birmingham City University recording 402 cases between 2022-24, while Robert Gordon University saw incidents skyrocket from 6 cases in 2022-23 to 205 in the following academic year—an increase of over 3,000%.
Study Mode: Technical Architecture and Pedagogical Approach
Study Mode transforms ChatGPT from an answer-providing engine into an interactive tutoring system based on established educational principles. The feature utilizes custom system instructions developed in collaboration with teachers, scientists, and pedagogy experts from over 40 institutions worldwide.
Core Features and Functionality
The system implements several key pedagogical approaches:
Socratic Questioning Method: Instead of providing direct answers, Study Mode engages students through guided questioning that encourages them to discover solutions independently. When a student asks for help with game theory, for example, the system first assesses their current knowledge level and learning objectives before providing customized explanations.
Scaffolded Learning: The feature breaks down complex information into structured, manageable sections with clear connections between concepts. This approach reduces cognitive overload while building understanding progressively.
Personalized Adaptation: Study Mode assesses users’ skill levels through diagnostic questions and adapts responses accordingly. It maintains memory of previous conversations, allowing for continuity and increasingly personalized learning experiences over time.
Active Knowledge Checks: The system regularly incorporates quizzes, open-ended questions, and reflection prompts to gauge understanding before progressing to new concepts.
System Architecture
The underlying technology relies on what OpenAI terms “custom system instructions” rather than a fundamentally different AI model. According to technical documentation revealed by researcher Simon Willison, the system prompt includes strict rules such as:
- “Be an approachable-yet-dynamic teacher, who helps the user learn by guiding them through their studies.”
- “Guide users, don’t just give answers. Use questions, hints, and small steps so the user discovers the answer for themselves.”
- “Above all: DO NOT DO THE USER’S WORK FOR THEM”
This approach allows for rapid iteration and improvement based on user feedback while maintaining the core functionality of ChatGPT.
Educational Impact and Research Findings
The introduction of Study Mode comes amid growing research into AI’s effects on learning outcomes. Studies have shown mixed results regarding AI’s educational impact, with effectiveness largely dependent on how students engage with the technology.
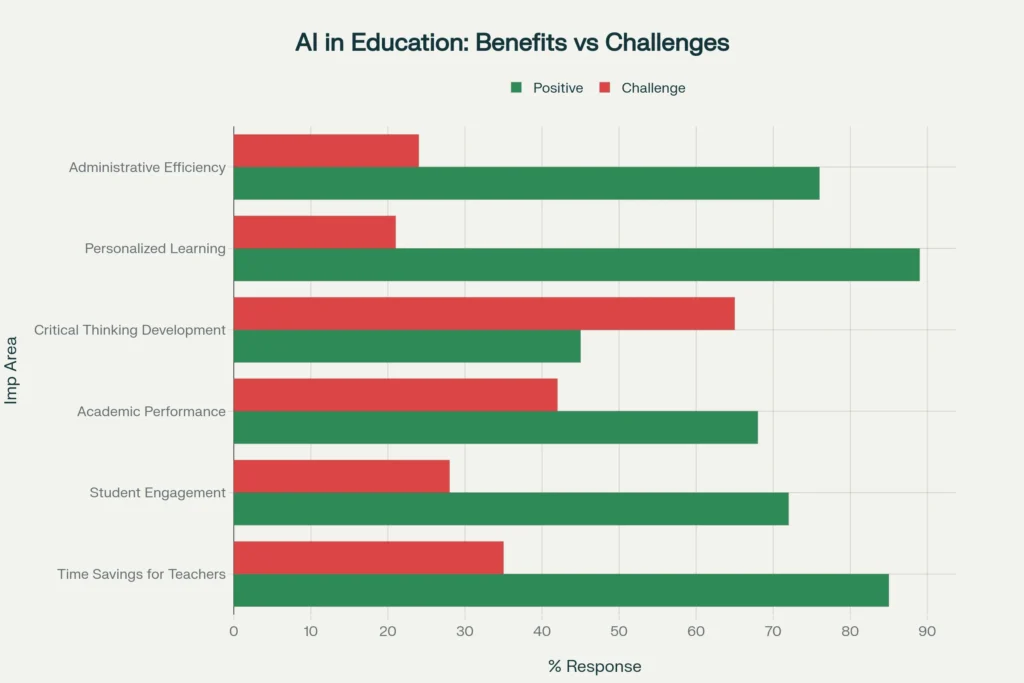
Comparison of positive impacts versus challenges of AI implementation across different areas of education
Positive Educational Outcomes
Research indicates that AI tutoring systems can significantly improve learning outcomes when properly implemented. A meta-analysis by Kulik and Fletcher found that AI tutors increased test scores by 0.66 standard deviations on average compared to traditional classroom instruction. Similarly, studies comparing intelligent tutoring systems to traditional teaching methods report effect sizes ranging from medium to large.
Recent research emphasizing mastery-oriented approaches shows promising results. Students who use AI to construct and augment knowledge—rather than simply regurgitate information—demonstrate significantly higher learning outcomes, including improved critical thinking, applied knowledge, and learning autonomy. These findings align with Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development theory, where AI serves as scaffolding to bridge gaps between students’ current abilities and their potential.
Challenges and Limitations
However, significant concerns persist. Studies reveal that students using ChatGPT to write essays exhibit lower brain activity compared to those using traditional research methods or Google Search. This suggests that AI may reduce the cognitive engagement necessary for deep learning.
Critical thinking development presents particular challenges, with only 45% of educators reporting positive impacts in this area, while 65% identify it as a significant concern. The risk of over-reliance remains substantial, with educators worried that AI dependency may atrophy essential problem-solving skills.
Academic integrity issues compound these concerns. Despite Study Mode’s safeguards, students can easily switch to regular ChatGPT if they become frustrated with the guided approach. OpenAI acknowledges this limitation, with VP of Education Leah Belsky stating, “If someone intends to circumvent the learning process and seek quick answers, that is feasible”.
Global Implementation and Institutional Responses
Availability and Rollout
Study Mode is available to all logged-in ChatGPT users across Free, Plus, Pro, and Team plans, with ChatGPT Edu integration planned for the coming weeks. The feature supports 11 Indian languages with comprehensive multimodal capabilities, including text, voice, and image interactions.
The global rollout represents OpenAI’s broader strategy to position itself as a responsible AI partner in education. The company has emphasized that Study Mode is “the first step” in a longer journey to improve learning outcomes through AI.
Institutional Partnerships and Initiatives
OpenAI’s educational strategy extends well beyond Study Mode through several major initiatives:
NextGenAI Consortium: Launched in March 2025 with a $50 million commitment, this partnership includes 15 leading research institutions such as Harvard, MIT, Oxford, and Duke University. The consortium aims to accelerate research breakthroughs and transform education through AI.
Teacher Training Initiative: In collaboration with the American Federation of Teachers, OpenAI committed $10 million over five years to train 400,000 K-12 teachers in AI usage. This National Academy for AI Instruction represents one of the largest professional development initiatives in education technology.
Canvas Integration: A partnership with Instructure brings OpenAI’s technology directly into the Canvas Learning Management System, used by millions of students globally. This integration allows educators to create custom AI experiences within existing educational workflows.
International Adoption Patterns
Educational institutions worldwide are adapting to AI integration at varying paces. UNESCO surveys reveal that fewer than 10% of schools and universities have developed formal AI guidance policies, leaving many educators to navigate implementation independently30. Universities show higher adoption rates than K-12 schools, with approximately 13% of higher education institutions having some form of AI policy compared to only 7% of schools.
Competitive Landscape and Industry Response
OpenAI’s Study Mode follows similar initiatives by competitors. Anthropic launched Learning Mode for its Claude chatbot in April 2024, while other educational technology companies have developed AI-powered tutoring systems. This represents a broader industry trend toward ethical AI deployment in educational contexts.
The competitive dynamics reflect growing recognition that educational AI tools must balance efficiency with pedagogical integrity. Companies are increasingly focusing on features that promote learning rather than task completion, responding to educator concerns about AI’s impact on critical thinking and academic integrity.
Limitations and Critical Perspectives
Despite its innovative approach, Study Mode faces several fundamental limitations:
Technical Limitations
OpenAI acknowledges that the current implementation may result in “inconsistent behavior and errors throughout conversations”. The reliance on system prompts rather than trained behaviors means that responses can vary unpredictably, potentially frustrating users seeking consistent guidance.
Pedagogical Concerns
Critics argue that Study Mode doesn’t address AI’s fundamental limitations in educational contexts. The system still relies on the same underlying knowledge base as regular ChatGPT, meaning it cannot distinguish reliable information from inaccuracies present in its training data. This poses particular risks in specialized subjects where precision is crucial.
Enforcement Challenges
The voluntary nature of Study Mode represents perhaps its greatest limitation. Students can easily switch to regular ChatGPT or other AI tools when seeking quick answers. Currently, no mechanisms exist for parents or administrators to lock students into Study Mode, though OpenAI has indicated this might be explored in the future.
Future Directions and Implications
Technological Evolution
OpenAI plans to integrate Study Mode behaviors directly into future AI models rather than relying on system prompts. This approach could provide more consistent and reliable educational interactions while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to different learning contexts.
Future enhancements may include visual explanations, goal-setting tools, deeper personalization, and conversation-based progress tracking. These developments could transform Study Mode from a simple tutoring interface into a comprehensive learning companion.
Educational Policy Implications
The introduction of Study Mode reflects broader questions about AI’s role in education. As institutions grapple with integration challenges, the success of tools like Study Mode may influence policy decisions about AI adoption, assessment methods, and academic integrity standards.
The effectiveness of Study Mode and similar tools will likely depend on comprehensive institutional approaches that combine technological solutions with updated pedagogical practices, teacher training, and clear ethical guidelines.
Research Gaps and Future Studies
While early feedback from students and educators appears positive, comprehensive longitudinal studies are needed to assess Study Mode’s actual impact on learning outcomes. Key research questions include:
- Does guided AI interaction improve long-term knowledge retention compared to traditional methods?
- How does Study Mode affect the development of critical thinking skills over extended periods?
- What are the optimal integration strategies for different educational contexts and subjects?
OpenAI has indicated plans to publish research findings as the tool evolves, potentially in collaboration with Stanford University’s SCALE Initiative.
Conclusion
OpenAI’s launch of Study Mode represents a significant evolution in how AI companies approach educational applications. By prioritizing guided learning over direct answers, the tool addresses some of the most pressing concerns about AI’s impact on academic integrity and critical thinking development.
However, Study Mode is not a panacea for the challenges AI poses in education. Its success will ultimately depend on broader institutional commitments to responsible AI integration, comprehensive teacher training, and the development of new assessment methods that account for AI’s capabilities.
The initiative reflects a crucial recognition that AI’s educational value lies not in replacing human learning processes but in augmenting them through thoughtful, pedagogically-informed design. As educational institutions worldwide continue to navigate the AI revolution, tools like Study Mode may provide a model for balancing technological innovation with educational integrity.
The long-term impact of Study Mode will depend on continued research, user feedback, and institutional adaptation. While it represents a promising step toward more responsible AI in education, it also highlights the complex challenges that remain in ensuring AI truly enhances rather than undermines the learning process.